China’s J-35A vs U.S. F-35: A Comprehensive Comparison. China‘s defense industry has rapidly evolved, achieving impressive milestones in the development of advanced military technologies. The most recent addition to China’s growing arsenal is the J-35A, a fifth-generation stealth fighter. While this aircraft has generated considerable attention, its full capabilities remain shrouded in mystery, leading to comparisons with the F-35, the United States’ multirole stealth fighter.
Introduction to the J-35A
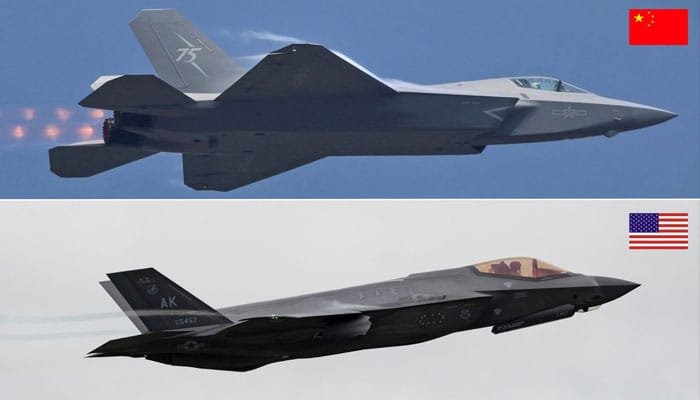
The J-35A, a stealth fighter developed by China’s Shenyang Aircraft Corporation, made its debut at the Zhuhai Air Show in November 2024. It is designed as a multi-role aircraft, capable of both air-superiority missions and ground strikes. This versatility is a testament to China’s growing aerospace capabilities, particularly given the progress made in just 25 years. Historically, Chinese pilots avoided flying at night or in poor weather, but with the introduction of the J-35A, China’s air force has taken a significant leap forward in terms of technology and operational capabilities.
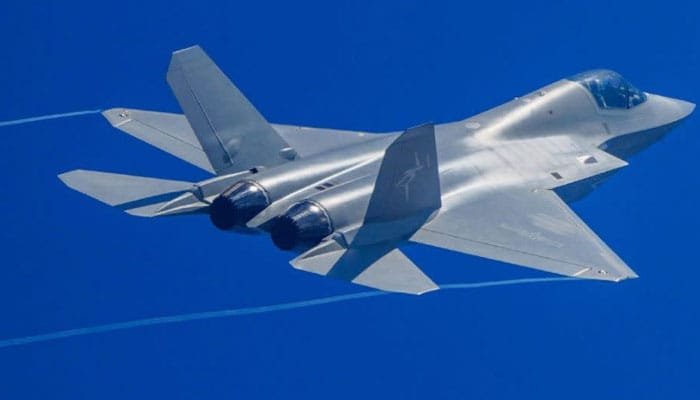

One key feature of the J-35A is its potential for carrier-based operations. This places it in the same category as the U.S. F-35C, the carrier variant of the Joint Strike Fighter. While the J-35A is not yet fully operational in this capacity, it signifies China’s ambition to modernize its navy by enhancing its aircraft carrier strike capabilities.
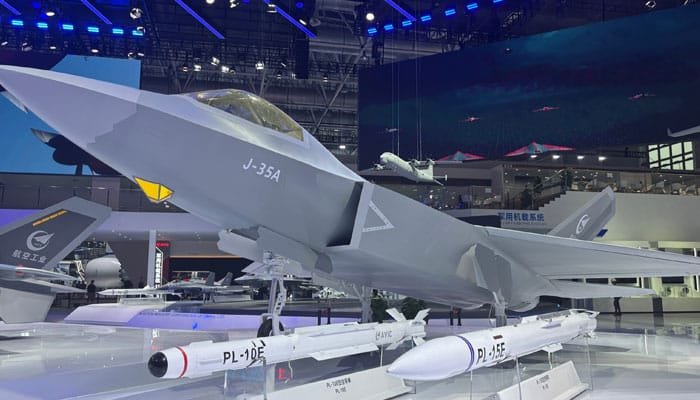

The Stealth Fighter Race: F-35 vs. J-35A
China’s J-35A is often compared to the American F-35, a fighter developed by Lockheed Martin. Both aircraft belong to the fifth generation of stealth fighters, but there are key differences in design, capabilities, and intended uses.
1. Stealth and Radar-Evasion Capabilities
Both the J-35A and the F-35 are equipped with stealth technology designed to minimize their radar cross-section, making them difficult to detect by enemy radar systems. However, there are differences in their stealth profiles.
F-35: The F-35 has been praised for its advanced stealth features, including a shape designed to reduce its radar signature and advanced radar-absorbing materials. It also features an integrated avionics suite that enhances its electronic warfare capabilities, making it one of the most radar-evading aircraft in the world.
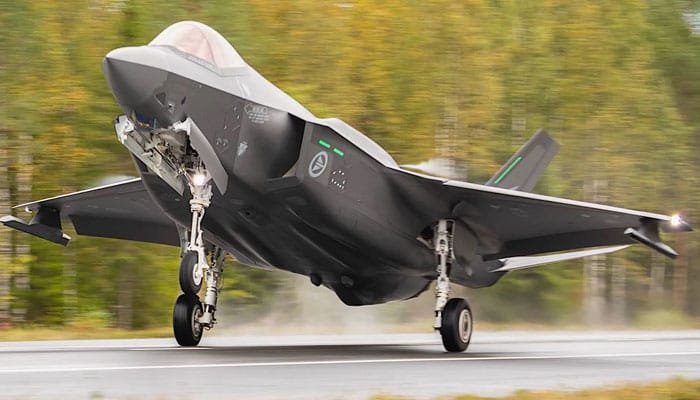

J-35A: While the J-35A is reported to have similar stealth characteristics, there is less certainty regarding its true radar-evading capabilities. Some experts believe that the J-35A may not be as stealthy as the F-35 due to its design differences. In particular, its airframe and engine exhaust design could be less optimized for low observability compared to the F-35.
2. Design and Versatility
F-35: The F-35 comes in three variants—F-35A (conventional takeoff and landing), F-35B (short takeoff and vertical landing), and F-35C (carrier-based). Its versatility allows it to perform a wide range of missions, from air superiority to close-air support and intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR). The F-35 is also designed for interoperability within NATO and with U.S. allies, making it a key asset in multinational operations.
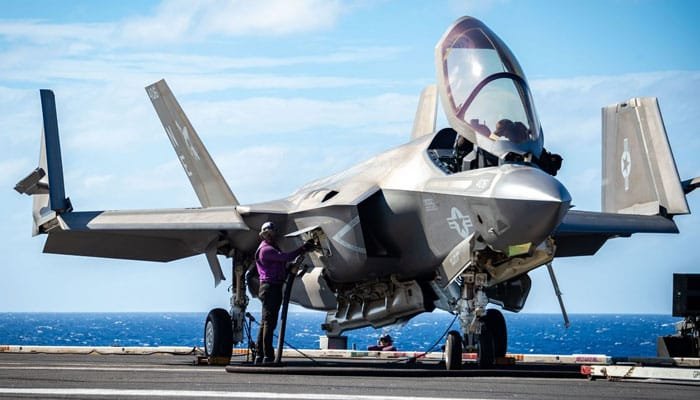

J-35A: The J-35A is primarily a multi-role fighter, with a focus on air superiority and ground strikes. While its design draws inspiration from the F-35, especially in its stealth features and size, it lacks the same level of versatility as the F-35. The J-35A’s true operational capabilities remain unclear, and it is still not fully clear whether it will match the broad operational flexibility of the F-35. However, China’s focus on developing carrier-based operations for the J-35A indicates that it could become a central piece of China’s naval strategy.
3. Engines and Performance
F-35: The F-35 features a single Pratt & Whitney F135 engine, which provides it with a top speed of approximately Mach 1.6. The aircraft is also known for its impressive maneuverability, a feature that makes it effective in dogfights, despite being primarily designed as a multirole stealth aircraft.
J-35A: The J-35A is believed to be powered by a more advanced engine, likely an improved version of the Russian-made RD-93 or a domestically developed engine. While performance specifications are not publicly available, reports suggest that the J-35A may have more powerful engines than earlier prototypes, potentially giving it enhanced speed and maneuverability. However, it is expected to have less agility compared to the F-35 due to differences in design and aerodynamics.
4. Avionics and Sensors
F-35: One of the F-35’s standout features is its advanced avionics suite, which includes radar systems such as the AN/APG-81 AESA radar. This provides superior situational awareness and can track multiple targets at long ranges. Additionally, the F-35 features advanced electronic warfare (EW) systems that can jam enemy radar and communications, making it a formidable asset in modern combat.
J-35A: While the exact specifications of the J-35A’s radar and sensors are not fully known, it is likely to feature modern radar systems with capabilities similar to the F-35. However, given China’s past allegations of cyber espionage, including accusations of stealing F-35 technology, some experts believe the J-35A may closely mirror the F-35’s avionics.
5. Role in Regional Security: China vs. the U.S.
F-35: The F-35 has been a cornerstone of U.S. defense strategy, offering unmatched capabilities for a wide range of missions. It has been deployed in multiple theaters around the world, from Europe to the Middle East, and is a key asset for NATO and U.S. allies in the Pacific.
J-35A: The J-35A’s primary role will likely be in regional security, particularly in the context of tensions between China and its neighbors, such as Taiwan, Japan, and South Korea. The J-35A could be deployed in scenarios ranging from defense of China’s airspace to more aggressive actions against Taiwan. Its stealth and potential for carrier-based operations make it a significant player in China’s efforts to assert dominance in the Indo-Pacific region.