What is the Biggest Continent on Earth? Asia is the largest continent on Earth in both land area and population. It occupies approximately 30% of the planet’s total land area and is home to more than 60% of the global population. With a landmass of about 44.58 million square kilometers, Asia surpasses all other continents in scale and diversity.
Top 10 Wealthiest Asian Countries to Explore in 2025. From manufacturing prowess in China to technological advancements in South Korea, here is a list of the richest countries in Asia to explore in 2025.
Geographic Scope & Borders
Asia stretches from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Indian Ocean in the south. It is bordered by Europe and Africa to the west and the Pacific Ocean to the east. Due to its sheer size, Asia spans multiple climate zones, from the frigid tundra of Siberia to the tropical rainforests of Southeast Asia.
Though geographically part of the same landmass as Europe, Asia is culturally and historically distinct. The two continents are often collectively referred to as “Eurasia,” but they are typically treated as separate entities in geopolitical and academic contexts.
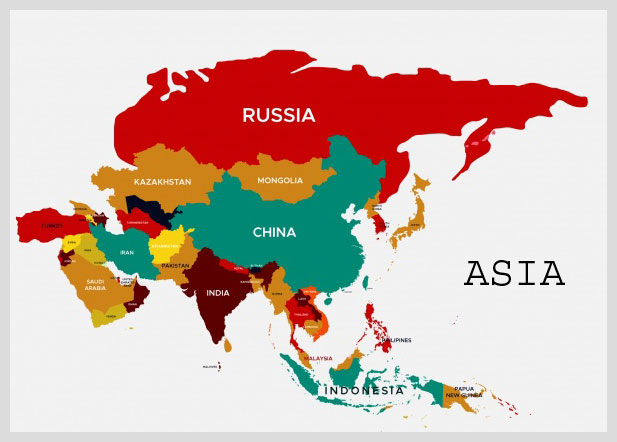
Countries & Population
Asia is composed of 49 countries, including major nations like China, India, Japan, Indonesia, and Russia (partly in Asia). The continent is also home to two of the most populous countries in the world: China and India, each with populations exceeding a billion people. Urban centers like Tokyo, Delhi, and Shanghai are among the largest metropolitan areas globally.
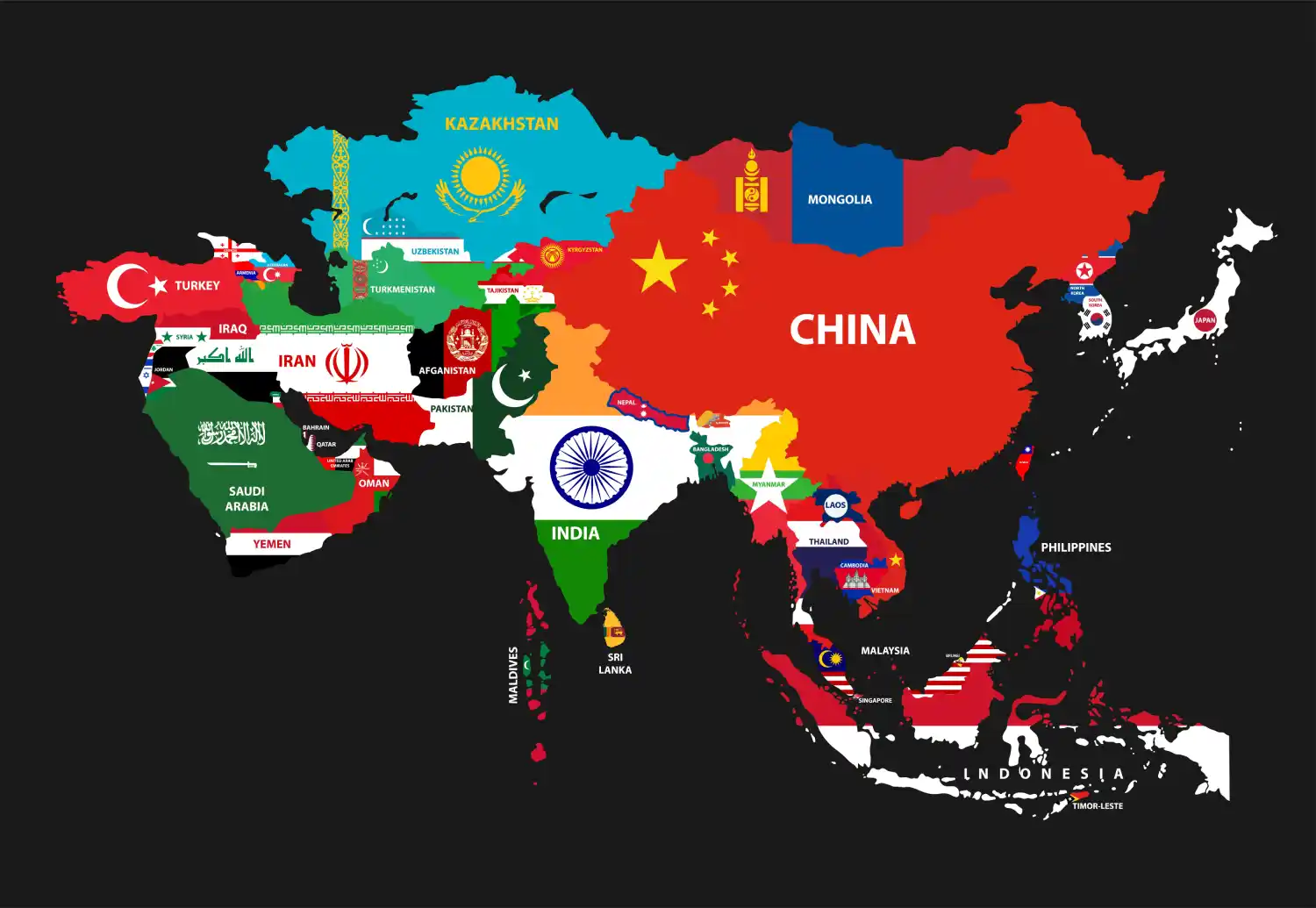

The population diversity is immense, including thousands of ethnic groups, languages, and cultural traditions. Major religions such as Hinduism, Buddhism, Islam, and many indigenous beliefs originated and thrive here.
Natural Resources & Biodiversity
Asia is rich in natural resources, including oil, natural gas, coal, minerals, and freshwater. Countries in the Middle East hold some of the world’s largest oil reserves, while regions like Siberia and Central Asia are abundant in minerals and timber.

Ecologically, Asia is home to some of the most biodiverse regions on the planet. Tropical rainforests, high-altitude mountain ranges, deserts, and marine environments contribute to an array of flora and fauna. Species like the giant panda, Bengal tiger, and orangutan are native to Asia and are critical to global biodiversity.
Economic Influence
Asia is a major driver of the global economy. Economies like China, Japan, India, and South Korea play leading roles in global trade, technology, and manufacturing. China is the world’s largest exporter, and India is a hub for IT services and innovation. The Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) and other regional trade agreements further strengthen Asia’s economic integration.

In recent decades, the continent has seen rapid industrialization, urban growth, and economic development, although disparities between developed and developing nations remain prominent.
Environmental Concerns & Sustainability
Despite its natural wealth, Asia faces significant environmental challenges. Rapid industrial growth has led to deforestation, air and water pollution, and loss of biodiversity. Climate change poses serious risks, especially to low-lying countries and island nations vulnerable to rising sea levels.
Green readability emphasizes sustainability, environmental awareness, and responsible resource use. In that context, Asia is making strides toward renewable energy adoption and sustainable development. China leads in solar and wind energy production, while countries like Bhutan maintain carbon-negative policies. International collaborations and environmental treaties are increasingly shaping policy decisions across the continent.
Conclusion
Asia stands as the largest and one of the most influential continents in the world. Its vast geographic span, diverse population, rich natural resources, and growing economic power place it at the center of global affairs. However, with great size comes great responsibility—Asia’s role in fostering sustainability and environmental stewardship is critical to the future of the planet. By embracing green readability principles and sustainable development goals, Asia has the potential to lead the world toward a more balanced and environmentally conscious future.